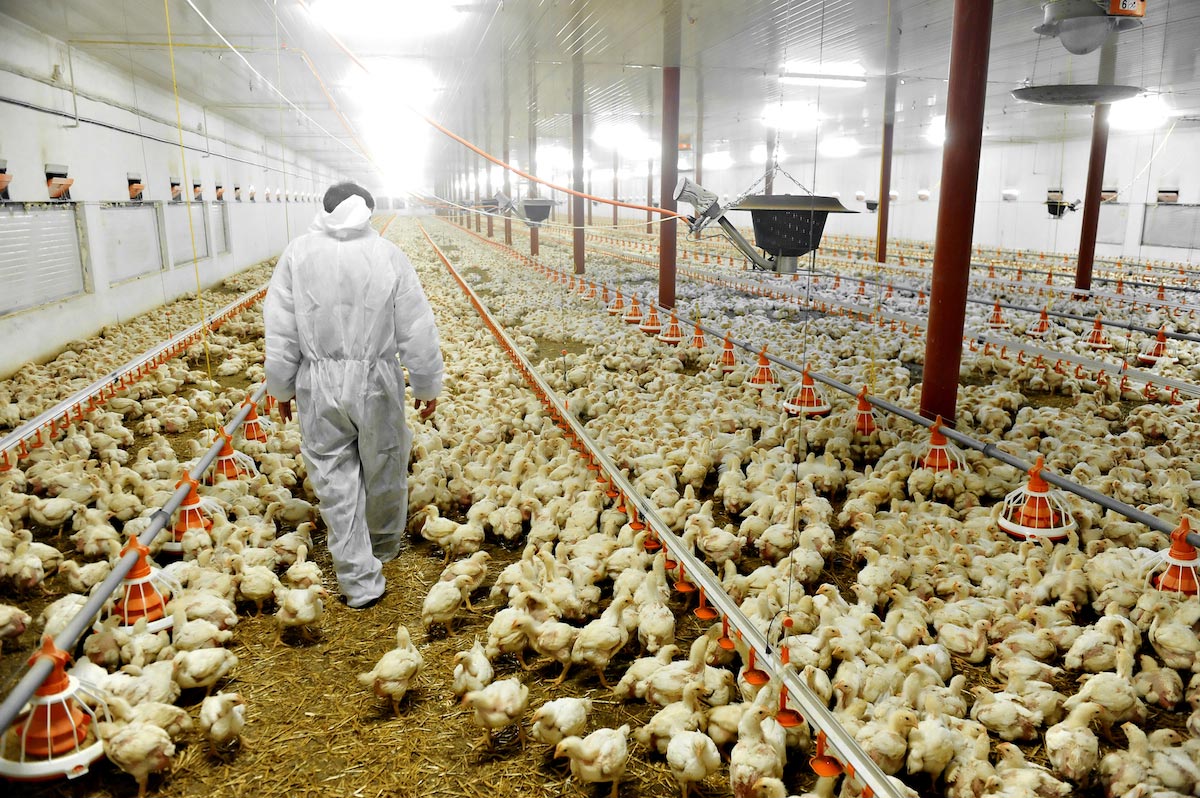
How Eating Animal Products Could Make Blood More Likely to Clot
by Julie Fidler, Natural Society:
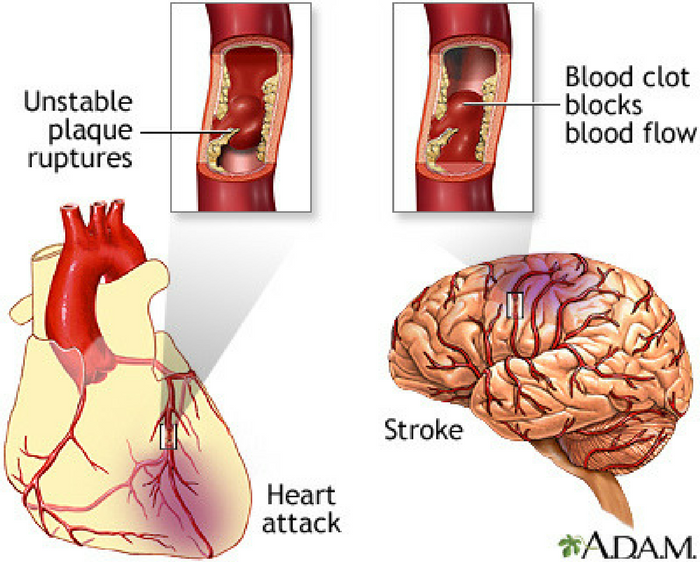
Researchers announced in April that they may have figured out how eating meat causes heart disease. The nutrient choline, an essential nutrient found in meat and eggs, may feed a certain gut bacteria which produce a compound that makes blood sticky and prone to form blood clots. These blood clots can lead to heart attacks and strokes. [1]
The study, led by Dr. Stanley Hazen of the Cleveland Clinic, was a small but intense one involving 18 participants – 8 who were either vegans or vegetarians and 10 who routinely ate meat, dairy, and eggs. Each volunteer was given a supplement of 500 mg of choline per day. The recommended daily choline intake for women is 425 mg, and for men it’s 550 mg.
After a month, the participants’ blood levels of a compound called trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) rose 10-fold. Tests showed that their blood became much more likely to form clots, leading the team to surmise that “TMAO supercharges platelet function.” Hazen added:
oth the vegans and the vegetarians had significantly lower choline levels at the beginning of the study than the meat-eaters did. Their levels were still much lower than the meat-eaters’ after taking choline supplements.
Read: 5 Benefits of Reducing Meat Consumption
The researchers did not find, however, that the volunteers who took the choline supplements had an actual higher risk of heart disease. The study did not last long enough or include enough participants to demonstrate such a conclusion.
But they did discover that other compounds found in animal products had a similar effect on gut bacteria. The team wrote:
“We previously showed gut microbial production of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) from dietary nutrients like choline, lecithin, and L-carnitine is linked to the development of cardiovascular diseases.” [1]