Bases, Bases, Everywhere … Except in the Pentagon’s Report
by Nick Turse, Consortium News:
 Within hours of President Trump’s announcement of a withdrawal of U.S. forces from Syria, equipment at that base was already being inventoried for removal. And just like that, arguably the most important American garrison in Syria was (maybe) being struck from the Pentagon’s books — except, as it happens, al-Tanf was never actually on the Pentagon’s books. Opened in 2015 and, until recently, home to hundreds of U.S. troops, it was one of the many military bases that exist somewhere between light and shadow, an acknowledged foreign outpost that somehow never actually made it onto the Pentagon’s official inventory of bases.
Within hours of President Trump’s announcement of a withdrawal of U.S. forces from Syria, equipment at that base was already being inventoried for removal. And just like that, arguably the most important American garrison in Syria was (maybe) being struck from the Pentagon’s books — except, as it happens, al-Tanf was never actually on the Pentagon’s books. Opened in 2015 and, until recently, home to hundreds of U.S. troops, it was one of the many military bases that exist somewhere between light and shadow, an acknowledged foreign outpost that somehow never actually made it onto the Pentagon’s official inventory of bases.
Officially, the Department of Defense maintains 4,775 “sites,” spread across all 50 states, eight U.S. territories, and 45 foreign countries. A total of 514 of these outposts are located overseas, according to the Pentagon’s worldwide property portfolio. Just to start down a long list, these include bases on the Indian Ocean island of Diego Garcia, in Djibouti on the Horn of Africa, as well as in Peru and Portugal, the United Arab Emirates, and the United Kingdom. But the most recent version of that portfolio, issued in early 2018 and known as the Base Structure Report (BSR), doesn’t include any mention of al-Tanf. Or, for that matter, any other base in Syria. Or Iraq. Or Afghanistan. Or Niger. Or Tunisia. Or Cameroon. Or Somalia. Or any number of locales where such military outposts are known to exist and even, unlike in Syria, to be expanding.
According to David Vine, author of “Base Nation: How U.S. Military Bases Abroad Harm America and the World,” there could be hundreds of similar off-the-books bases around the world. “The missing sites are a reflection of the lack of transparency involved in the system of what I still estimate to be around 800 U.S. bases outside the 50 states and Washington, D.C., that have been encircling the globe since World War II,” says Vine, who is also a founding member of the recently established Overseas Base Realignment and Closure Coalition, a group of military analysts from across the ideological spectrum who advocate shrinking the U.S. military’s global “footprint.”
Such off-the-books bases are off the books for a reason. The Pentagon doesn’t want to talk about them. “I spoke to the press officer who is responsible for the Base Structure Report and she has nothing to add and no one available to discuss further at this time,” Pentagon spokesperson Lieutenant Colonel Michelle Baldanza told TomDispatch when asked about the Defense Department’s many mystery bases.
“Undocumented bases are immune to oversight by the public and often even Congress,” Vine explains. “Bases are a physical manifestation of U.S. foreign and military policy, so off-the-books bases mean the military and executive branch are deciding such policy without public debate, frequently spending hundreds of millions or billions of dollars and potentially getting the U.S. involved in wars and conflicts about which most of the country knows nothing.”
Where Are They?
The Overseas Base Realignment and Closure Coalition notes that the United States possesses up to 95 percent of the world’s foreign military bases, while countries like France, Russia, and the United Kingdom have perhaps 10-20 foreign outposts each. China has just one.
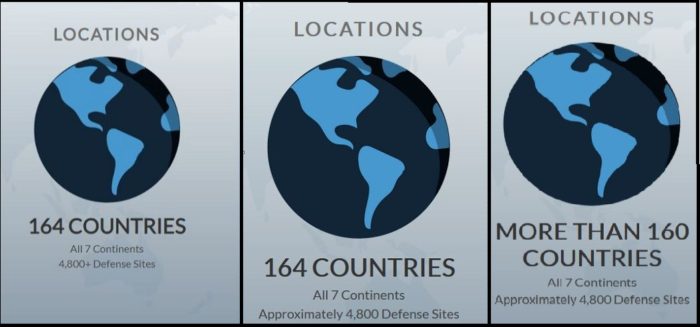
The Department of Defense even boasts that its “locations” include 164 countries. Put another way, it has a military presence of some sort in approximately 84 percent of the nations on this planet — or at least the DoD briefly claimed this. After TomDispatch inquired about the number on a new webpage designed to tell the Pentagon’s “story” to the general public, it was quickly changed. “We appreciate your diligence in getting to the bottom of this,” said Lieutenant Colonel Baldanza. “Thanks to your observations, we have updated defense.gov to say ‘more than 160.’”
The progressive changes made to the Defense Department’s “Our Story” webpage as a result of questions from TomDispatch.
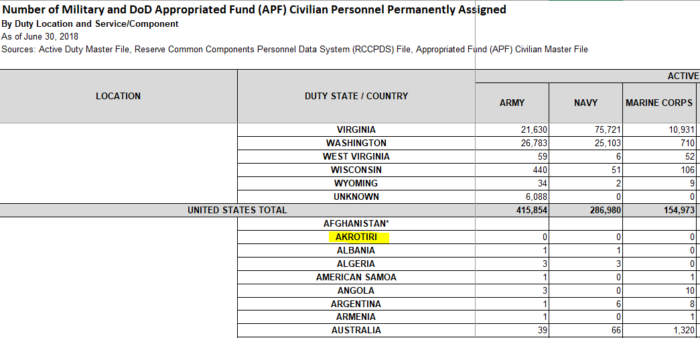
What the Pentagon still doesn’t say is how it defines a “location.” The number 164 does roughly track with the Department of Defense’s current manpower statistics, which show personnel deployments of varying sizes in 166 “overseas” locales — including some nations with token numbers of U.S. military personnel and others, like Iraq and Syria, where the size of the force was obviously far larger, even if unlisted at the time of the assessment. (The Pentagon recently claimed that there were 5,200 troops in Iraq and at least 2,000 troops in Syria although that number should now markedly shrink.) The Defense Department’s “overseas” tally, however, also lists troops in U.S. territories like American Samoa, Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Wake Island. Dozens of soldiers, according to the Pentagon, are also deployed to the country of “Akrotiri” (which is actually a village on the island of Santorini in Greece) and thousands more are based in “unknown” locations.
In the latest report, the number of those “unknown” troops exceeds 44,000.
Official Defense Department manpower statistics show U.S. forces deployed to the nation of “Akrotiri.”
The annual cost of deploying U.S. military personnel overseas, as well as maintaining and running those foreign bases, tops out at an estimated $150 billion annually, according to the Overseas Bases Realignment and Closure Coalition. The price tag for the outposts alone adds up to about one-third of that total. “U.S. bases abroad cost upwards of $50 billion per year to build and maintain, which is money that could be used to address pressing needs at home in education, health care, housing, and infrastructure,” Vine points out.
Perhaps you won’t be surprised to learn that the Pentagon is also somewhat fuzzy about just where its troops are stationed. The new Defense Department website, for instance, offered a count of “4,800+ defense sites” around the world. After TomDispatch inquired about this total and how it related to the official count of 4,775 sites listed in the BSR, the website was changed to read “approximately 4,800 Defense Sites.”
“Thank you for pointing out the discrepancy. As we transition to the new site, we are working on updating information,” wrote Lieutenant Colonel Baldanza. “Please refer to the Base Structure Report which has the latest numbers.”
In the most literal sense, the Base Structure Report does indeed have the latest numbers — but their accuracy is another matter. “The number of bases listed in the BSR has long born little relation to the actual number of U.S. bases outside the United States,” says Vine. “Many, many well-known and secretive bases have long been left off the list.”
Read More @ ConsortiumNews.com
Loading...