CIA Was So Focused On Developing Cyber Weapons That "Woefully Lax" Security Led To Vault 7 Leak
The CIA's Center for Cyber Intelligence (CCI) was so busy making cyber weapons - including tools to crack into smartphones, hijack smart TVs, or make it look like a foreign adversary hacked someone - that they internal security become "woefully lax," allowing a CIA employee to steal up to 34 terabytes of information later published by WikiLeaks in the spring of 2017.
According to a report created by the CIA's WikiLeaks Task Force in 2017 and released Tuesday by Sen. Ron Wyden (D-OR) on Tuesday, there were major security lapses at CCI.
"In a press to meet growing and critical mission needs, CCI had prioritized building cyber weapons at the expense of securing their own systems," reads the report. "Day-to-day security practices had become woefully lax."
"CCI focused on building cyber weapons and neglected to also prepare mitigation packages if those tools were exposed. These shortcomings were emblematic of a culture that evolved over years that too often prioritized creativity and collaboration at the expense of security," the report continues.
The leak marked the largest data breach in the CIA’s history and included information on hacking tools used by the agency to break into smartphones and other internet-connected devices.
The task force noted that due to failures to address vulnerabilities in IT systems, if WikiLeaks had not published the stolen information, the CIA “might still be unaware of the loss — as would be true for the vast majority of data on Agency mission systems.”
In a letter to Director of National Intelligence John Ratcliffe on Tuesday, Wyden criticized the intelligence community for its “widespread cybersecurity problems.” -The Hill
The Vault 7 release - a series of 24 documents which began to publish on March 7, 2017 - reveal that the CIA has a giant arsenal of tools to use against adversaries, including the ability to "spoof" its malware to appear as though it was created by a foreign intelligence agency, as well as the ability to take control of Samsung Smart TV's and surveil a target using a "Fake Off" mode in which they appear to be powered down while eavesdropping.
The CIA's toy chest also includes:
- Tools code named "Marble" - which can misdirect forensic investigators from attributing viruses, trojans and hacking attacks to their agency by inserted code fragments in foreign languages. The tool was in use as recently as 2016. Per the WikiLeaks release:
"The source code shows that Marble has test examples not just in English but also in Chinese, Russian, Korean, Arabic and Farsi. This would permit a forensic attribution double game, for example by pretending that the spoken language of the malware creator was not American English, but Chinese, but then showing attempts to conceal the use of Chinese, drawing forensic investigators even more strongly to the wrong conclusion, --- but there are other possibilities, such as hiding fake error messages."
CIA's "Marble Framework" shows its hackers use potential decoy languages https://t.co/Hm3pTPSXIS
Background: https://t.co/GsoN4BuyTz pic.twitter.com/ZT66doCnfY
— WikiLeaks (@wikileaks) March 31, 2017
- iPads / iPhones / Android devices and Smart TV’s are all susceptible to hacks and malware. The agency's "Dark Matter" project reveals that the CIA has been bugging “factory fresh” iPhones since at least 2008 through suppliers. Another, "Sonic Screwdriver" allows the CIA to execute code on a Mac laptop or desktop while it's booting up.
RELEASE: CIA #Vault7 "Dark Matter" https://t.co/pgnfeODXVB pic.twitter.com/vkI16f3vMD
— WikiLeaks (@wikileaks) March 23, 2017
RELEASE: CIA #Vault7 "Sonic Screwdriver" https://t.co/pgnfeODXVB pic.twitter.com/18BcVdqkqd
— WikiLeaks (@wikileaks) March 23, 2017
- The increasing sophistication of surveillance techniques has drawn comparisons with George Orwell’s 1984, but “Weeping Angel”, developed by the CIA’s Embedded Devices Branch (EDB), which infests smart TVs, transforming them into covert microphones, is surely its most emblematic realization.
- The Obama administration promised to disclose all serious vulnerabilities they found to Apple, Google, Microsoft, and other US-based manufacturers. The US Government broke that commitment.
"Year Zero" documents show that the CIA breached the Obama administration's commitments. Many of the vulnerabilities used in the CIA's cyber arsenal are pervasive and some may already have been found by rival intelligence agencies or cyber criminals.
In addition to its operations in Langley, Virginia the CIA also uses the U.S. consulate in Frankfurt as a covert base for its hackers covering Europe, the Middle East and Africa.
CIA hackers operating out of the Frankfurt consulate ( "Center for Cyber Intelligence Europe" or CCIE) are given diplomatic ("black") passports and State Department cover.
- The CIA laughs at Anti-Virus / Anti-Malware programs.
CIA hackers developed successful attacks against most well known anti-virus programs. These are documented in AV defeats, Personal Security Products, Detecting and defeating PSPs and PSP/Debugger/RE Avoidance. For example, Comodo was defeated by CIA malware placing itself in the Window's "Recycle Bin". While Comodo 6.x has a "Gaping Hole of DOOM".
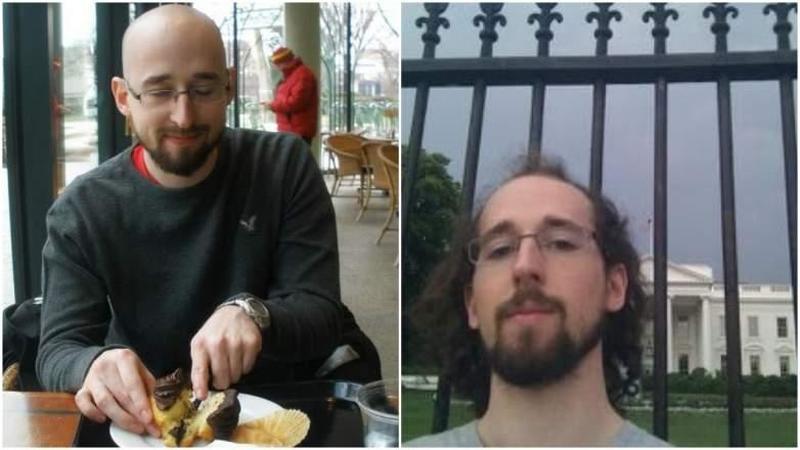
In March, the trial of former CIA computer engineer Joshua Schulte ended in a hung jury on eight counts, including illegal gathering and transmission of national defense information, according to the New York Times.
Schulte was convicted on two other counts; contempt of court and making false statements to the FBI. He awaits trial on unrelated charges of possessing, receiving and transporting child pornography.